package org.opentutorials.javatutorials.eclips;
public class PrePostDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 4-3*6;
System.out.println(a);
//console -> -14
}
}
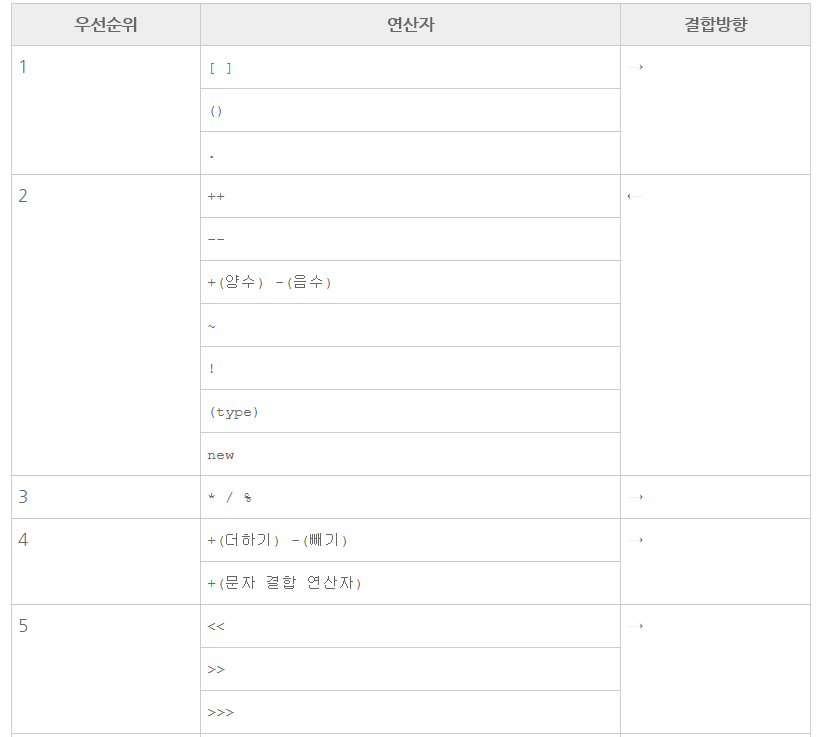
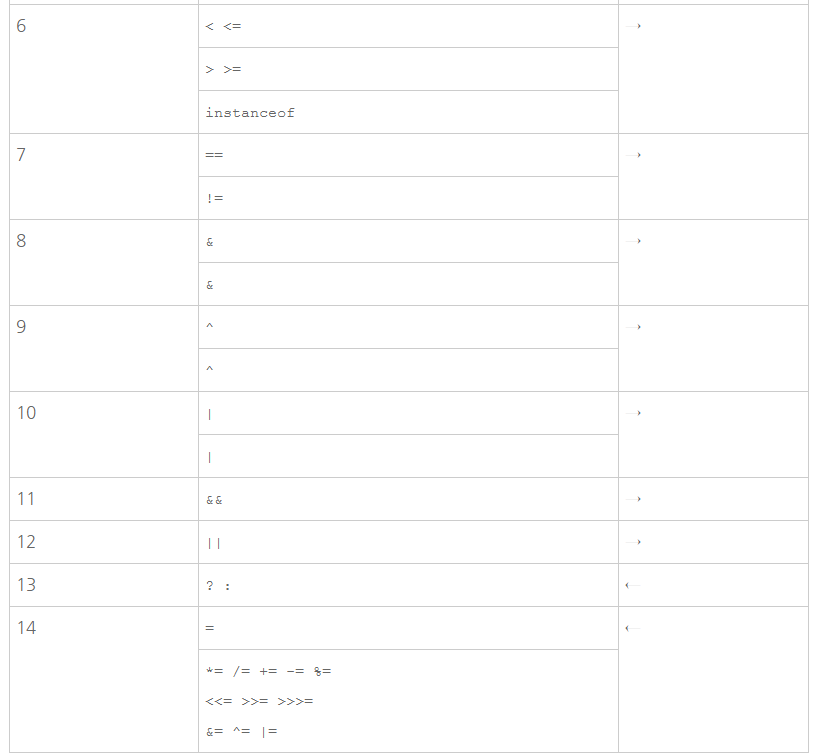
위의 구문에는 3가지의 연산자가 등장한다. =, -, * 이다.
표에 따라서 우선순위 별로 배열해보면 *, -, =가 된다. 그러므로 연산자 *가 제일 먼저 실행된다.
따라서 첫 번째 연산은 3*6이 된다. 그 값은 18이다.
그 다음 우선순위는 -다.
4-18을 해야 하는데 빼기의 결합 방향은 →이다. 따라서 4에서 18을 빼야 한다.
그 결과는 -14가 된다.
그다음 우선순위는 대입 연산자인 '='이다.
'='의 결합방향은 '←'이기 때문에 -14를 변수 a에 대입해서 연산이 끝나게 된다.
위의 표를 외울 필요는 없다. 자연스럽게 이해하게 된다.
다만, 헷갈리는 경우가 있을 때 이 표의 도움을 받도록 하자.
+추가 코드
package org.opentutorials.javatutorials.eclips;
public class PrePostDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 3;
i++;
System.out.println(i);
++i;
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(++i);
System.out.println(i++);
System.out.println(i);
/* int value = 0;
* value++; (증감연산자)
* System.out.println(value);
*
* console -> 1
*/
/* Comparison Operator
* int a = 10, b = 20;
* System.out.println(a<b);
* System.out.println(a>b);
*
* console -> True/ False
* 비교연산자의 경우 참이면 1(true), 거짓이면 0(False)를 반환시킴
*/
}
}
'PL(ProgrammingLanguage) > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 조건문 (if) (0) | 2021.02.28 |
|---|---|
| Boolean과 Comparison Operator (0) | 2021.02.28 |
| 연산자(형변환) (0) | 2021.02.26 |
| 산술연산자(Arithmetic Operator) (0) | 2021.02.26 |
| 연산자 (0) | 2021.02.18 |